As a leading financial institution in the South African Region, UBG has to implement reliable information system. In a service oriented organization like UBG, customers' satisfaction and security are among the most important factor should be considered in selecting a Transaction Processing System (TPS).
The Branch Delivery System (BDS) was introduced in 1999 to replace the older TPS known as the PB Olifin. The earlier version of BDS supports all type of operational transactions like deposits, withdrawals and transfers of funds. However, the BDS functionalities have been expanded progressively with the arrival of new banking products.
BDS runs on the Windows operating system. On top of it is the NCR proprietary security and functional layer call Extended Security System (ESS). The ESS application provides controls on the usage of authorized software on the system and it also manages the distribution and update of program to branches.
The workstation consists of a computer loaded with Branch View Client Software (BV), which is the subsystem of BDS. Each computer is attached with a Pin Pad Magnetic Stripe Reader and a Document Printer for transaction slips, vouchers and passbooks. In addition, there is also a Laser Printer connected to the Local Area Network (LAN). Another important hardware in a BDS LAN is a resilient server (Branch View Server). Configured with RAID 1 technology and equipped with additional hard disk and LAN card.
BDS serves as the operation system at UBG Branches and some head office's departments. Transaction such as deposit, withdrawals, transfers, loan or credit card repayments and service charges can be done at any BDS workstation.
Every teller and approving supervisors are assigned with a unique User/Teller ID number. This ID has a unique password that can't be used by other staff including superiors. It allows the teller to perform transactions on customers' accounts.
Beside the User/Teller ID number, each approving supervisor is also assigned with Supervisor Override Cards. The card holds the power to approve exceptional accounts and transactions. For example, any transaction above $50,000.00 will require Supervisor Override. There are many other reasons that may require Supervisor Override. A register is also maintained by Operations Manager to record staff acknowledgements on User/Teller ID and Supervisor Override Cards issued.
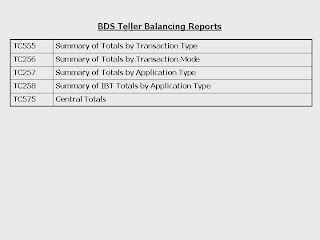
It can be hundreds of various transactions by a teller during each business day. Hence, day end report will be printed for the teller balancing purposes. The total deposits and withdrawals transactions reflected in this report should agree to the physical cheques and cash holding by the teller. A supervisor will also countercheck each copy of transaction slips to ensure the inputs were correct and accurate.
Part of the BDS services is generating a series of end day summary reports that show total transaction of the day according to its type. An exceptional report of transactions with huge amounts will also be printed for the Operations Manager's attention. The day correction report shows all the error correction transactions performed by all tellers, which should be checked and signed by all responsible supervisors for early detection of frauds.
Automated Teller Machines (ATM), Cash Deposit Machines (CDM) and Cheques Deposit Machines are other TPS that can be found at UBG. These machines offer banking services to customers 24 hours. ATM allows customers to withdraw cash, CDM allow customers to bank in cash and Cheques Deposit Machines accept cheques deposits at any time. Even though these machines are not operated by human, the maintenance and monitoring are handled by the bank's personnel. All transactions performed are transmitted directly into the bank's database and will appear in a series of reports and journal roll for verification and balancing by officer in charge.